As the world transitions towards a sustainable future, the need for clean energy technologies has become more pressing than ever. One such technology that has gained significant attention in recent years is the proton exchange membrane (PEM), which has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and store energy.
What is a Proton Exchange Membrane?
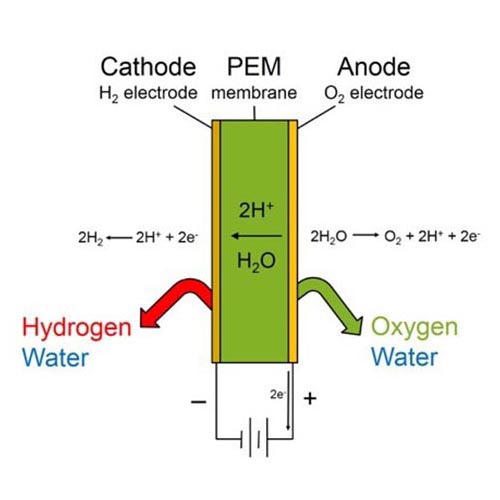
A proton exchange membrane is a thin, flexible material that allows for the passage of protons while blocking the passage of other particles. It is made up of a polymer electrolyte, which provides the necessary conductivity for protons to flow through it. PEMs are commonly used in fuel cells, which convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity and water. They are also used in electrolyzers, which split water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity.
How Does it Work?
PEMs work by separating the hydrogen ions (protons) from the electrons in a hydrogen molecule. The protons are then allowed to flow through the membrane, while the electrons are directed through an external circuit to generate electricity. This process produces only water as a byproduct, making it a clean and sustainable energy source.
Advantages of PEMs
One of the main advantages of PEMs is their high efficiency. They can convert up to 60% of the energy in hydrogen into electricity, making them more efficient than traditional combustion engines. PEMs are also lightweight, compact, and quiet, making them ideal for use in portable devices and vehicles.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its many advantages, PEM technology still faces some challenges. One of the main challenges is the cost of the materials used to make the membrane. However, research is underway to develop more cost-effective materials that can be produced on a larger scale.
The proton exchange membrane is a breakthrough technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and store energy. As the world continues to move towards a sustainable future, PEMs will play a critical role in helping us achieve our goals of reducing carbon emissions and building a cleaner, more sustainable world.