Electrolysis is a process that has been around for over 200 years, but it is only now that we are truly unlocking its power. Anion exchange membranes are a key component in the efficient electrolysis of water, allowing us to produce hydrogen on a large scale. This is an important development, as hydrogen is a clean and renewable energy source that has the potential to revolutionize the way we power our homes and vehicles.
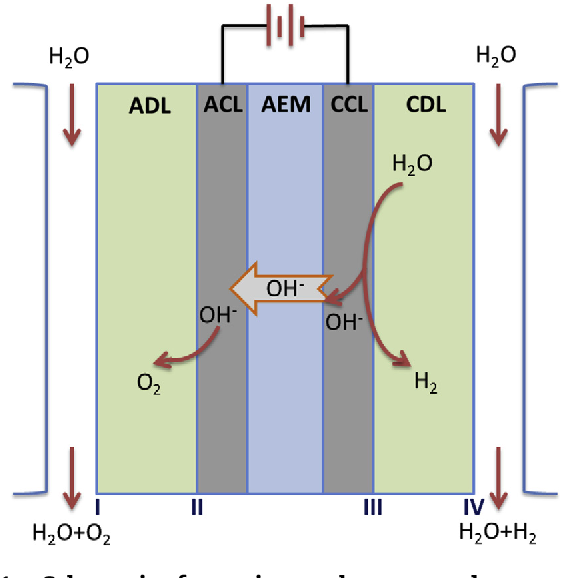
Anion exchange membranes are made from a polymer that has a positively charged backbone and negatively charged functional groups. These functional groups attract the negatively charged ions in the electrolyte solution, allowing only the positively charged ions to pass through. This creates a barrier that separates the anode and cathode chambers, preventing the mixing of gases and the formation of unwanted byproducts.
One of the main advantages of using anion exchange membranes is that they are highly selective, allowing for the efficient separation of hydrogen and oxygen gases. This is important because it means that we can produce high-purity hydrogen, which is essential for many industrial applications. Additionally, anion exchange membranes are highly stable and can withstand the harsh conditions of electrolysis, making them ideal for use in large-scale industrial processes.
Another advantage of anion exchange membranes is that they can be easily integrated into existing electrolysis systems. This means that we can retrofit existing plants with anion exchange membranes, allowing us to increase their efficiency and reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, anion exchange membranes can be used with a variety of different electrolytes, including alkaline and acidic solutions, making them highly versatile.
Overall, anion exchange membranes are a key component in the efficient electrolysis of water, allowing us to produce high-purity hydrogen on a large scale. They offer many advantages over other types of membranes, including high selectivity, stability, and ease of integration. As we continue to unlock the power of anion exchange membranes, we are sure to see even more exciting developments in the field of electrolysis.