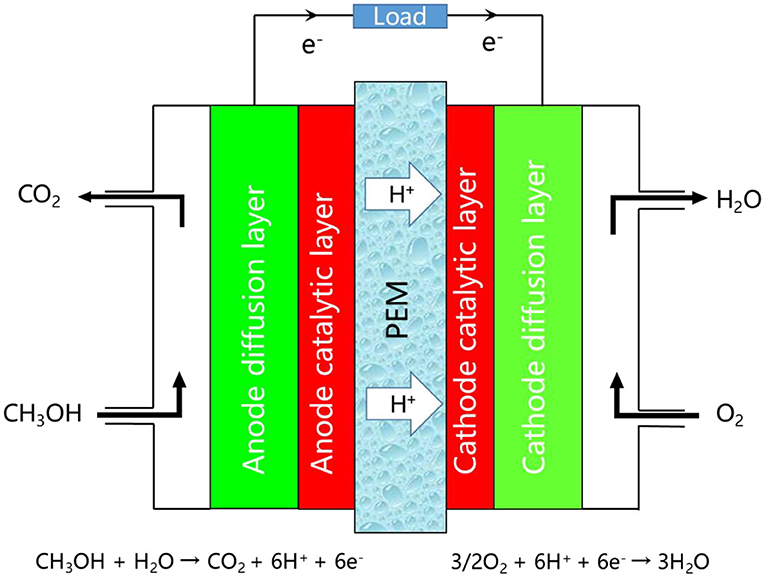
The Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) is a key component in many electrochemical devices, including fuel cells, electrolyzers, and redox flow batteries. The advantages of using PEMs are as follows:
- High Efficiency: PEMs are highly efficient in converting chemical energy into electrical energy. They have a high-power density and can achieve high conversion efficiencies, making them suitable for various applications.
- Fast Start-up: PEMs can start quickly, making them ideal for mobile applications such as automotive and portable power devices.
- Low Temperature Operation: PEMs operate at relatively low temperatures, typically between 60-100°C, which results in low thermal stress and fast start-up times.
- Clean Energy Production: PEMs use hydrogen or other renewable sources to produce electricity, resulting in clean energy production with no harmful emissions.
- Scalability: PEMs can be easily scaled up or down to meet various power requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Durability: PEMs have a long lifespan, with high resistance to chemical and physical degradation, and they can operate in harsh environments.
The use of PEMs has the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions and increase the efficiency of energy conversion, making them an attractive option for a wide range of energy applications.