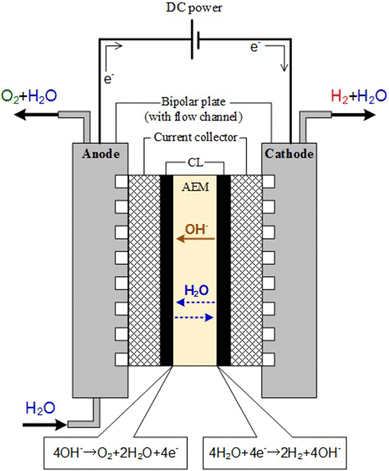
Anion exchange membrane (AEM) is a type of polymer membrane that has the ability to conduct negatively charged ions while blocking the passage of positively charged ions. AEM has recently gained attention as a promising technology for revolutionizing clean energy production, particularly in fuel cells and electrolyzers. Here are some advantages and applications of AEM in clean energy:
- Advantages of AEM
- AEM-based devices operate at low temperatures and pressures, which reduces the need for expensive and complex materials.
- AEM has higher alkaline stability than other types of membranes, which means it can withstand higher pH environments.
- AEM is more resistant to fouling and scaling, which reduces the need for frequent membrane cleaning.
- AEM is a cost-effective solution, as it can be produced at a lower cost than other types of membranes.
- Applications of AEM:
- Fuel cells: AEM fuel cells are a promising technology for clean energy production. They use hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to produce electricity, with water as the only byproduct. AEM fuel cells have the potential to be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional proton exchange membrane fuel cells.
- Electrolyzers: AEM electrolyzers are a type of device that uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process is known as electrolysis, and the resulting hydrogen gas can be used as a clean and renewable energy source. AEM electrolyzers have the potential to be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional proton exchange membrane electrolyzers.
- Carbon capture: AEM can be used as a membrane in carbon capture devices to separate CO2 from flue gas. AEM-based carbon capture devices have the potential to be more efficient and cost-effective than traditional amine-based carbon capture technologies.
Anion exchange membrane technology has the potential to revolutionize clean energy production by offering cost-effective, efficient, and scalable solutions for fuel cells, electrolyzers, and carbon capture devices.